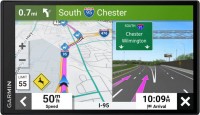
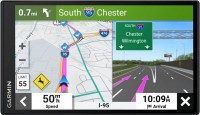
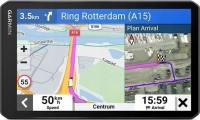
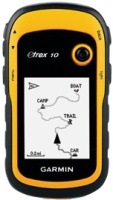
Sat Navs Garmin
All Sat Navs Advanced filters → |
You might be interested in
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials
Car protection: the functionality of modern car alarms
The current generation of “signaling” has acquired a mass of functions tied to enhanced resistance to car theft

Smartphone navigation: global satellite navigation systems GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and Beidou
There are four global satellite navigation systems in the world that operate on similar principles.
Sat Navs: specifications, types
Application area
— For passenger cars. Navigators designed for installation in passenger cars. As a rule, they are supposed to be installed on the windshield so that the screen is constantly in front of the driver’s eyes. Power is most often supplied through the cigarette lighter socket. Pre-installed cards, if any, are “tailored” for driving specifically in a passenger car - they contain data on the type and quality of roads, the characteristics of crossings and junctions, and other road factors.
— For trucks. Devices for navigation and routing of trucks. Such models often take into account the design features of trucks, on the basis of which suitable routes are built, taking into account restrictions on weight, height, length, width and other factors. Also, navigators for cargo vehicles can take into account specific rules of different countries such as speed limits, travel time, etc.
— For campers. Navigators for motorhomes, caravans and campers. Models of this type take into account specific features that may be important when traveling on a camper: length, dimensions, weight and other technical parameters of the “motorhome”. Maps in such navigators provide safe routes to travel, taking into account potential restrictions, contain information about camping parks, waste water disposal sites, gas stations, attractions, etc.
— Motorcycles.... Motorcycle navigators are designed to be attached to the handlebars and, as a rule, have enhanced moisture and shock protection, allowing them to withstand the effects of atmospheric precipitation without consequences and withstand impacts and shocks when driving. In such models, screens measuring from 3 " diagonally are installed; power supply from 6 V or 12 V is often provided, which allows you to connect the navigator to the motorcycle’s on-board power supply and save battery power. The software part includes functions related to road traffic - the same ones found in navigators for cars (see the corresponding paragraph). Also, the Bluetooth function is very popular in motorcycle models (see “Interfaces”) - in this embodiment, it allows you to display voice prompts on a headset under the helmet or built into the helmet.
- Tourist. Tourist GPS navigators are designed primarily for hiking and are intended for tourism. The main set of cards for such devices are routes of various tourist destinations, attractions or hiking trails. Most of these models are initially intended to be carried in your pocket, like a smartphone or other similar gadget. They often provide a waterproof case and a good built-in battery for long battery life.
— Wrist. Wrist navigators are aimed at athletes and partly tourists. They are attached to the wrist using a special strap. The display of such models is predominantly monochrome, which is done to reduce energy consumption, and the set of cards is released with an emphasis on walking (or jogging). In addition to navigation tools, they can be equipped with functions for measuring heart rate and a fitness calculator.
— For trucks. Devices for navigation and routing of trucks. Such models often take into account the design features of trucks, on the basis of which suitable routes are built, taking into account restrictions on weight, height, length, width and other factors. Also, navigators for cargo vehicles can take into account specific rules of different countries such as speed limits, travel time, etc.
— For campers. Navigators for motorhomes, caravans and campers. Models of this type take into account specific features that may be important when traveling on a camper: length, dimensions, weight and other technical parameters of the “motorhome”. Maps in such navigators provide safe routes to travel, taking into account potential restrictions, contain information about camping parks, waste water disposal sites, gas stations, attractions, etc.
— Motorcycles.... Motorcycle navigators are designed to be attached to the handlebars and, as a rule, have enhanced moisture and shock protection, allowing them to withstand the effects of atmospheric precipitation without consequences and withstand impacts and shocks when driving. In such models, screens measuring from 3 " diagonally are installed; power supply from 6 V or 12 V is often provided, which allows you to connect the navigator to the motorcycle’s on-board power supply and save battery power. The software part includes functions related to road traffic - the same ones found in navigators for cars (see the corresponding paragraph). Also, the Bluetooth function is very popular in motorcycle models (see “Interfaces”) - in this embodiment, it allows you to display voice prompts on a headset under the helmet or built into the helmet.
- Tourist. Tourist GPS navigators are designed primarily for hiking and are intended for tourism. The main set of cards for such devices are routes of various tourist destinations, attractions or hiking trails. Most of these models are initially intended to be carried in your pocket, like a smartphone or other similar gadget. They often provide a waterproof case and a good built-in battery for long battery life.
— Wrist. Wrist navigators are aimed at athletes and partly tourists. They are attached to the wrist using a special strap. The display of such models is predominantly monochrome, which is done to reduce energy consumption, and the set of cards is released with an emphasis on walking (or jogging). In addition to navigation tools, they can be equipped with functions for measuring heart rate and a fitness calculator.
Water protection IPX7
Devices with water resistance "7" according to the IP standard.
Water protection of this level allows the possibility of complete immersion of the GPS navigator under water, but for a short period of time and at a shallow depth. Specific restrictions on these indicators may be different – they need to be clarified separately. Instead of the letter "X" in the designation of dust and water protection, there may be a number that determines the resistance of the device case to dust and foreign objects. Water protection level "7" is combined with dust protection levels of at least 5 (it is allowed to get inside a small amount of dust that does not affect the operation of the device), and more often 6 (complete dust tightness). Specifically, the IPX7 marking means that this model has not been tested for dust resistance and has been certified only for water resistance. However, if water cannot get inside, then it is all the more difficult for dust.
Water protection of this level allows the possibility of complete immersion of the GPS navigator under water, but for a short period of time and at a shallow depth. Specific restrictions on these indicators may be different – they need to be clarified separately. Instead of the letter "X" in the designation of dust and water protection, there may be a number that determines the resistance of the device case to dust and foreign objects. Water protection level "7" is combined with dust protection levels of at least 5 (it is allowed to get inside a small amount of dust that does not affect the operation of the device), and more often 6 (complete dust tightness). Specifically, the IPX7 marking means that this model has not been tested for dust resistance and has been certified only for water resistance. However, if water cannot get inside, then it is all the more difficult for dust.
Pre-installed soft
The navigation programme, originally installed in the navigator and sold with it, in other words, a set of maps available to the user “out of the box”.
Most modern navigators are equipped with such programs (although the name of pre-installed maps is not indicated for all models). Note that the functionality of complete programs in different models may vary. Most often, these are the simplest maps of the world or the region in which this device is sold. However, there are exceptions: there are models with detailed maps, programs with advanced functionality, etc. Such exceptions are especially common among high-end specialized devices, in particular marine and aviation (see "Scope"). And for some navigators, there may be several options for pre-installed programs and even the ability to select such programs at the request of the user. All these details should be specified in each case according to the manufacturer or seller.
It is also worth considering that the characteristics often indicate only the general name of the cards. At the same time, the same card can be available in several versions that differ in functionality and, sometimes, terms of use (paid / free). However, the main features are basic capabilities, interface device, etc. — usually, are common to all versions. Therefore, by the name of the complete programme, usually, one can quite accurately determine the general capabilities and features of the card's functionality.
Most modern navigators are equipped with such programs (although the name of pre-installed maps is not indicated for all models). Note that the functionality of complete programs in different models may vary. Most often, these are the simplest maps of the world or the region in which this device is sold. However, there are exceptions: there are models with detailed maps, programs with advanced functionality, etc. Such exceptions are especially common among high-end specialized devices, in particular marine and aviation (see "Scope"). And for some navigators, there may be several options for pre-installed programs and even the ability to select such programs at the request of the user. All these details should be specified in each case according to the manufacturer or seller.
It is also worth considering that the characteristics often indicate only the general name of the cards. At the same time, the same card can be available in several versions that differ in functionality and, sometimes, terms of use (paid / free). However, the main features are basic capabilities, interface device, etc. — usually, are common to all versions. Therefore, by the name of the complete programme, usually, one can quite accurately determine the general capabilities and features of the card's functionality.
Map coverage
The region of the world for which map data is available on your navigation device. Map coverage determines which geographic areas and countries can be displayed and used for navigation on a specific device. Note that coverage may vary in detail and content: some preset maps may contain detailed information about roads, landmarks, shops, gas stations and the like on a global scale, while others are often limited to the basic road network for a particular country or region .
To make it easier to find a suitable solution for map coverage, registrars can be divided into several subcategories based on territoriality: Europe, Africa, the whole world.
To make it easier to find a suitable solution for map coverage, registrars can be divided into several subcategories based on territoriality: Europe, Africa, the whole world.
Lifetime map updates
Availability of life-long updating of maps in this model of the navigator.
When buying a navigator with this feature, the user also acquires a subscription to map updates supplied in the kit. Such a subscription, in fact, is perpetual: updates are available all the time while the navigator is generally working. Thus, this service allows you to always have the latest maps at your disposal. It is found mainly in automotive and motorcycle models: it is for these areas of application that regular updates are most relevant, since traffic conditions can change very quickly. However note that the cost of subscribing to updates is included in the price of the device and affects it, sometimes quite noticeably.
When buying a navigator with this feature, the user also acquires a subscription to map updates supplied in the kit. Such a subscription, in fact, is perpetual: updates are available all the time while the navigator is generally working. Thus, this service allows you to always have the latest maps at your disposal. It is found mainly in automotive and motorcycle models: it is for these areas of application that regular updates are most relevant, since traffic conditions can change very quickly. However note that the cost of subscribing to updates is included in the price of the device and affects it, sometimes quite noticeably.
Number of routes
The maximum number of routes that can be entered into the memory of the GPS navigator.
The ability to save routes is convenient, first of all, for those who regularly have to travel the same roads: instead of laying the path anew each time, it is enough to select the appropriate route in the navigator's memory. As for the number of "remembered" routes, in modern navigators it can reach several hundred, but large amounts of memory cost accordingly. Therefore, when choosing according to this parameter, one should take into account real needs: for example, it is hardly worth specifically looking for a model for 50 routes or more if your regular trips are limited to 5-6 places in the city and 2-3 places outside the city.
The ability to save routes is convenient, first of all, for those who regularly have to travel the same roads: instead of laying the path anew each time, it is enough to select the appropriate route in the navigator's memory. As for the number of "remembered" routes, in modern navigators it can reach several hundred, but large amounts of memory cost accordingly. Therefore, when choosing according to this parameter, one should take into account real needs: for example, it is hardly worth specifically looking for a model for 50 routes or more if your regular trips are limited to 5-6 places in the city and 2-3 places outside the city.
Waypoints
The maximum number of waypoints that can be stored in the navigator.
A waypoint is a point on the map with specific coordinates set by the user. Such points can be used both to mark individual important places (work / home, regularly visited institutions in the city, camps or springs in nature, etc.), and when laying routes (it is convenient to designate intermediate points through which you must pass the route). The more points the navigator is able to "remember" — the wider its capabilities; in the most advanced models, this number can reach 10,000 or even more. On the other hand, extensive memory will also cost more.
A waypoint is a point on the map with specific coordinates set by the user. Such points can be used both to mark individual important places (work / home, regularly visited institutions in the city, camps or springs in nature, etc.), and when laying routes (it is convenient to designate intermediate points through which you must pass the route). The more points the navigator is able to "remember" — the wider its capabilities; in the most advanced models, this number can reach 10,000 or even more. On the other hand, extensive memory will also cost more.
Navigation functions (assistants)
Special navigation functions provided in the device.
— Speed limit. A function that allows you to use the navigator to obtain information about the speed limit on a particular road. Most often, the speed limit is used in the operational prompt mode: the device warns the driver in advance about approaching a section of the road where the speed limit differs from the current one, and also issues a warning if the driver accelerates above the permissible limit. This can prevent not only an unpleasant conversation with the traffic police, but also a serious accident.
— Traffic jams in real time. A function that allows the driver to see real-time traffic data on the device screen. As a rule, models with a traffic monitoring function provide detailed information about the volume of traffic in general. Moreover, this information is monitored and updated constantly, in real time, and is immediately taken into account by the navigator - to the point that if difficulties arise on a pre-planned route, the device can automatically reroute it to avoid congestion. At the same time, it is worth considering that real-time traffic data is usually transmitted through the TMC network (see “TMC receiver”), and it is not available everywhere.
— GPS informant. A function to provide the driver with various useful information related to the current location. In acc...ordance with the name, the coordinates are determined using GPS. One of the most common ways to use an informant is to warn about approaching traffic cameras, stationary traffic police posts and speed control systems. In addition, other functions may be provided - for example, informing about entering a section of the road with a high accident rate or a separate large hole on the roadway. To operate the GPS informer, a database of relevant objects is entered into the device’s memory. When purchasing a navigator, it doesn’t hurt to clarify what exactly this database contains, how recent it is, and whether it can be updated.
— Lane selection. A function that provides the driver with hints regarding lane selection. Such tips make driving more convenient and safe: the navigator warns the driver in advance about the need to change lanes for a turn/turn (or vice versa, in order to drive straight past the turn). This allows you to avoid “misses” on the road and emergency lane changes, which often create emergency situations. This function is especially relevant for complex interchanges on multi-lane highways.
— Parking in real time. As its name suggests, this feature allows you to determine if there are nearby parking options for your vehicle. In addition, navigators that support the real-time parking function are also capable of displaying various auxiliary information, for example, type of parking, parking cost, payment methods, etc.
— The way back. The function of using a record of the distance traveled as a route to return from the finish point to the start point. Thanks to it, the customer can go back the same way he got to the current point. This opportunity is especially important in conditions of difficult terrain and the absence of roads - for example, during hiking trips or off-road jeep trips: returning along an already explored path is often easier and safer than looking for a new route. Actually, the opposite way is found mainly among universal pocket navigators (see “Scope of Application”), although there are exceptions - for example, the same car models.
- “Where am I?”. A function that helps the customer determine their current location. At the same time, we are talking not only about a point on the map and geographic coordinates - in addition to this data, the navigator, when you turn on the “Where am I?” function. displays various additional information: the address of the nearest building, information about the nearest intersection, nearby important objects (gas stations, hospitals, police stations, etc.).
— Prices at gas stations in real time. A function that provides information about current fuel prices at various gas stations along your travel route. It can be useful for drivers, as it allows them to find the most profitable or nearest gas stations to refuel and save money.
— Weather in real time. A feature that allows the navigator to receive real-time weather data. This can be either information about current weather conditions in a particular place on the map, or a forecast for a certain period. In addition to basic weather information (temperature, fit, wind, humidity, fog, etc.), this service can support advanced data such as storm warnings, flood or landslide reports. The necessary data can arrive in different ways - most often through a satellite or a special radio channel. These details should be clarified separately.
- Supervision of children. A function that allows the driver to use the navigator screen to observe the rear seat of the car without turning around and without being distracted from the road. Most often it is used to monitor a child who is in the back seat. Of course, to use the child monitoring function you will need not only a navigator, but also a camera compatible with it.
— Speed limit. A function that allows you to use the navigator to obtain information about the speed limit on a particular road. Most often, the speed limit is used in the operational prompt mode: the device warns the driver in advance about approaching a section of the road where the speed limit differs from the current one, and also issues a warning if the driver accelerates above the permissible limit. This can prevent not only an unpleasant conversation with the traffic police, but also a serious accident.
— Traffic jams in real time. A function that allows the driver to see real-time traffic data on the device screen. As a rule, models with a traffic monitoring function provide detailed information about the volume of traffic in general. Moreover, this information is monitored and updated constantly, in real time, and is immediately taken into account by the navigator - to the point that if difficulties arise on a pre-planned route, the device can automatically reroute it to avoid congestion. At the same time, it is worth considering that real-time traffic data is usually transmitted through the TMC network (see “TMC receiver”), and it is not available everywhere.
— GPS informant. A function to provide the driver with various useful information related to the current location. In acc...ordance with the name, the coordinates are determined using GPS. One of the most common ways to use an informant is to warn about approaching traffic cameras, stationary traffic police posts and speed control systems. In addition, other functions may be provided - for example, informing about entering a section of the road with a high accident rate or a separate large hole on the roadway. To operate the GPS informer, a database of relevant objects is entered into the device’s memory. When purchasing a navigator, it doesn’t hurt to clarify what exactly this database contains, how recent it is, and whether it can be updated.
— Lane selection. A function that provides the driver with hints regarding lane selection. Such tips make driving more convenient and safe: the navigator warns the driver in advance about the need to change lanes for a turn/turn (or vice versa, in order to drive straight past the turn). This allows you to avoid “misses” on the road and emergency lane changes, which often create emergency situations. This function is especially relevant for complex interchanges on multi-lane highways.
— Parking in real time. As its name suggests, this feature allows you to determine if there are nearby parking options for your vehicle. In addition, navigators that support the real-time parking function are also capable of displaying various auxiliary information, for example, type of parking, parking cost, payment methods, etc.
— The way back. The function of using a record of the distance traveled as a route to return from the finish point to the start point. Thanks to it, the customer can go back the same way he got to the current point. This opportunity is especially important in conditions of difficult terrain and the absence of roads - for example, during hiking trips or off-road jeep trips: returning along an already explored path is often easier and safer than looking for a new route. Actually, the opposite way is found mainly among universal pocket navigators (see “Scope of Application”), although there are exceptions - for example, the same car models.
- “Where am I?”. A function that helps the customer determine their current location. At the same time, we are talking not only about a point on the map and geographic coordinates - in addition to this data, the navigator, when you turn on the “Where am I?” function. displays various additional information: the address of the nearest building, information about the nearest intersection, nearby important objects (gas stations, hospitals, police stations, etc.).
— Prices at gas stations in real time. A function that provides information about current fuel prices at various gas stations along your travel route. It can be useful for drivers, as it allows them to find the most profitable or nearest gas stations to refuel and save money.
— Weather in real time. A feature that allows the navigator to receive real-time weather data. This can be either information about current weather conditions in a particular place on the map, or a forecast for a certain period. In addition to basic weather information (temperature, fit, wind, humidity, fog, etc.), this service can support advanced data such as storm warnings, flood or landslide reports. The necessary data can arrive in different ways - most often through a satellite or a special radio channel. These details should be clarified separately.
- Supervision of children. A function that allows the driver to use the navigator screen to observe the rear seat of the car without turning around and without being distracted from the road. Most often it is used to monitor a child who is in the back seat. Of course, to use the child monitoring function you will need not only a navigator, but also a camera compatible with it.
Bands number
The number of communication channels supported by the navigator.
One communication channel allows the device to receive one operating frequency from one satellite. Without going into unnecessary details, we can say that the greater the number of channels, the more efficient the navigator works (including in dense urban areas and other adverse conditions) and the less time it takes for a “cold” start. On the other hand, numerous supported frequencies complicates the receiver and increases its cost.
As for the specific number, 12 channels are needed to work effectively with GPS, but today such receivers are considered obsolete and are almost never used. Most low-cost receivers support about 20 channels (there are also more modest solutions, at 16 or even 14 frequencies), mid-range solutions have about 30 – 40 channels, and in advanced models this number is most often 64 or 66 (although sometimes more) .
One communication channel allows the device to receive one operating frequency from one satellite. Without going into unnecessary details, we can say that the greater the number of channels, the more efficient the navigator works (including in dense urban areas and other adverse conditions) and the less time it takes for a “cold” start. On the other hand, numerous supported frequencies complicates the receiver and increases its cost.
As for the specific number, 12 channels are needed to work effectively with GPS, but today such receivers are considered obsolete and are almost never used. Most low-cost receivers support about 20 channels (there are also more modest solutions, at 16 or even 14 frequencies), mid-range solutions have about 30 – 40 channels, and in advanced models this number is most often 64 or 66 (although sometimes more) .
GLONASS support
The ability of the navigator to work with the GLONASS satellite navigation system. GLONASS (GLOBAL NAVIGATION Sputnik System) is a Russian navigation system, the only currently functioning alternative to the American GPS. It has been in full operation since October 2011. By itself, GLONASS has a slightly lower accuracy than GPS, so it is rarely used in its “pure” form — usually navigators receive signals from both satellite systems at once. This format provides positioning accuracy up to 1.5 m. In addition, the ability of the navigator to work with GLONASS provides reliability in the event of a failure or failure of one of the navigation systems (although unlikely, but theoretically possible).
Galileo support
Galileo is a European satellite navigation system designed as an alternative to American GPS. Note that it is under the control of civilian departments, not the military. With a full fleet of 24 active satellites, the system gives an accuracy of up to 1 m in public mode and up to 20 cm with the GHA service. Working in conjunction with GPS, the Galileo system provides a more accurate position measurement, especially in densely populated areas.
DAB receiver
The presence of a DAB receiver in the design of the navigator.
The abbreviation DAB stands for Digital Broadcasting. This is the key difference between this standard and other popular formats (including FM known to many): the radio signal during such broadcasting is transmitted in digital form, using the MP2 codec.
Digital broadcasting has a number of advantages over analogue broadcasting. So, in a similar way, you can achieve a greater range with a lower power of transmitters, and without loss in quality. Actually, the sound quality in DAB does not depend on the strength of the received signal; to be more precise, weak interference does not affect its quality, and if the power drops to a critical level, the sound is not distorted, but disappears completely. The disadvantage of this standard is its relatively low prevalence; therefore, before buying a navigator with DAB, it is worth checking whether there is a digital broadcast in your area and what are the technical requirements for receivers for such broadcasting.
The abbreviation DAB stands for Digital Broadcasting. This is the key difference between this standard and other popular formats (including FM known to many): the radio signal during such broadcasting is transmitted in digital form, using the MP2 codec.
Digital broadcasting has a number of advantages over analogue broadcasting. So, in a similar way, you can achieve a greater range with a lower power of transmitters, and without loss in quality. Actually, the sound quality in DAB does not depend on the strength of the received signal; to be more precise, weak interference does not affect its quality, and if the power drops to a critical level, the sound is not distorted, but disappears completely. The disadvantage of this standard is its relatively low prevalence; therefore, before buying a navigator with DAB, it is worth checking whether there is a digital broadcast in your area and what are the technical requirements for receivers for such broadcasting.
TMC receiver
The presence of a TMC receiver in the design of the navigator.
TMC (Traffic Message Channel) is a technology for transmitting information about adverse traffic situations — traffic jams, accidents, weather conditions, etc. Transmissions are most often carried out in the FM band, similar to conventional radio broadcasting; therefore, you do not need to access the Internet to obtain important traffic information, although some TMC services may be chargeable.
It is worth bearing in mind that a network of appropriate stations is required to use TMC. Such networks exist in many European countries, but their development in the post-Soviet space began relatively recently. Therefore, before buying a navigator with this function, you need to check whether TMC coverage is available in your area.
TMC (Traffic Message Channel) is a technology for transmitting information about adverse traffic situations — traffic jams, accidents, weather conditions, etc. Transmissions are most often carried out in the FM band, similar to conventional radio broadcasting; therefore, you do not need to access the Internet to obtain important traffic information, although some TMC services may be chargeable.
It is worth bearing in mind that a network of appropriate stations is required to use TMC. Such networks exist in many European countries, but their development in the post-Soviet space began relatively recently. Therefore, before buying a navigator with this function, you need to check whether TMC coverage is available in your area.
Display
Parameters of the display installed in the navigator.
— Display diagonal. Size screen size in inches. The larger the screen, the more information can be displayed on it and the more detailed this information will be presented. On the other hand, the size of the display significantly affects the dimensions of the device, and large screens are more expensive.
— Display resolution. Display size in dots (pixels) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution (with the same diagonal), the more detailed and clear the image the screen can produce. In addition, on high-resolution displays, small details are better visible, which increases the comfort of viewing information. Too high a resolution is usually not required for GPS navigator displays: for example, 800x480 pixels, limited by the standards of smartphones or tablets, with a diagonal screen size of about 6” are considered quite sufficient even for an advanced device.
— Matrix type. This parameter is indicated mainly for tech cases when the screen uses a high-quality IPS type matrix. This technology provides high quality color rendering, good brightness and wide viewing angles; moreover, IPS screens are relatively inexpensive to produce.
- Touch. Screen support for touch control. You can give commands to the device by touching the icons on the display itself - similar to how this is done in smartphones and tablets. Touch control opens up...many more possibilities than classic controls and provides flexibility in working with the navigator. In particular, by touching the screen you can set points on the route, zoom in or out on the map, etc.
- Color. This parameter determines whether the screen is color or monochrome (black and white). Black and white displays are simple, inexpensive, consume little power, and are quite suitable for displaying basic navigation information. At the same time, color screens are more functional: maps often use different colors to highlight individual objects, which would not be possible on monochrome displays. As a result, black and white screens are quite rare among modern navigators - mainly among the most compact and inexpensive models.
— Backlight. The screen has its own backlight system. This function makes the device independent of external lighting: the illuminated image will be normally visible both at dusk and even in complete darkness. It is also worth noting that many LCD screens have a backlight by default; it is activated when the screen itself is turned on and works regardless of external lighting - without it, the image on the matrix would simply be impossible to see. In particular, this operating principle is used in IPS-type matrices, which have gained popularity in modern portable electronics (including navigators).
— Display diagonal. Size screen size in inches. The larger the screen, the more information can be displayed on it and the more detailed this information will be presented. On the other hand, the size of the display significantly affects the dimensions of the device, and large screens are more expensive.
— Display resolution. Display size in dots (pixels) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution (with the same diagonal), the more detailed and clear the image the screen can produce. In addition, on high-resolution displays, small details are better visible, which increases the comfort of viewing information. Too high a resolution is usually not required for GPS navigator displays: for example, 800x480 pixels, limited by the standards of smartphones or tablets, with a diagonal screen size of about 6” are considered quite sufficient even for an advanced device.
— Matrix type. This parameter is indicated mainly for tech cases when the screen uses a high-quality IPS type matrix. This technology provides high quality color rendering, good brightness and wide viewing angles; moreover, IPS screens are relatively inexpensive to produce.
- Touch. Screen support for touch control. You can give commands to the device by touching the icons on the display itself - similar to how this is done in smartphones and tablets. Touch control opens up...many more possibilities than classic controls and provides flexibility in working with the navigator. In particular, by touching the screen you can set points on the route, zoom in or out on the map, etc.
- Color. This parameter determines whether the screen is color or monochrome (black and white). Black and white displays are simple, inexpensive, consume little power, and are quite suitable for displaying basic navigation information. At the same time, color screens are more functional: maps often use different colors to highlight individual objects, which would not be possible on monochrome displays. As a result, black and white screens are quite rare among modern navigators - mainly among the most compact and inexpensive models.
— Backlight. The screen has its own backlight system. This function makes the device independent of external lighting: the illuminated image will be normally visible both at dusk and even in complete darkness. It is also worth noting that many LCD screens have a backlight by default; it is activated when the screen itself is turned on and works regardless of external lighting - without it, the image on the matrix would simply be impossible to see. In particular, this operating principle is used in IPS-type matrices, which have gained popularity in modern portable electronics (including navigators).
Video resolution
Resolution of the video recorded by the built-in video recorder of the navigator
The higher the video resolution, other things being equal, the more detailed the video is, the better you can see the small details of what is happening on it. This is especially important when analyzing traffic accidents or ambiguous situations, as well as identifying people, fixing car numbers, etc. On the other hand, higher resolution requires more powerful hardware and more capacious drives for storing footage — all this has a corresponding effect on the price of the device.
The higher the video resolution, other things being equal, the more detailed the video is, the better you can see the small details of what is happening on it. This is especially important when analyzing traffic accidents or ambiguous situations, as well as identifying people, fixing car numbers, etc. On the other hand, higher resolution requires more powerful hardware and more capacious drives for storing footage — all this has a corresponding effect on the price of the device.
Frame rate
The frame rate at which the built-in DVR can capture video.
The higher the frame rate, ceteris paribus, the smoother the image, the less fast moving objects are blurred, and the more accurately you can make out the details in dynamic scenes (including freeze frames). On the other hand, a high frame rate increases the power requirements of the electronic hardware. Therefore, in navigators, this indicator usually does not exceed 30 fps — this provides a fairly good shooting quality with relatively low hardware requirements.
The higher the frame rate, ceteris paribus, the smoother the image, the less fast moving objects are blurred, and the more accurately you can make out the details in dynamic scenes (including freeze frames). On the other hand, a high frame rate increases the power requirements of the electronic hardware. Therefore, in navigators, this indicator usually does not exceed 30 fps — this provides a fairly good shooting quality with relatively low hardware requirements.
Field of view
Viewing angle of the built-in video recorder installed in the navigator.
The size of the space covered by the camera directly depends on the viewing angle: the wider the angle, the larger the size of the area that enters the frame, and the less likely it is to miss an object or event located on the periphery of the frame. On the other hand, ceteris paribus, an increase in the viewing angle gives the effect of reducing the picture — individual details look smaller and are less clearly visible. And at too wide angles, noticeable distortions appear on the edges of the image.
Speaking about the specific values of the angles, it is worth noting that the minimum indicator found among the registrars is about 50 ° — this is comparable to the field of view and the degree of magnification of the human eye (excluding side vision). The maximum viewing angle can theoretically reach 180°, however, in fact, navigators use cameras with more modest characteristics — mainly up to 120°.
The size of the space covered by the camera directly depends on the viewing angle: the wider the angle, the larger the size of the area that enters the frame, and the less likely it is to miss an object or event located on the periphery of the frame. On the other hand, ceteris paribus, an increase in the viewing angle gives the effect of reducing the picture — individual details look smaller and are less clearly visible. And at too wide angles, noticeable distortions appear on the edges of the image.
Speaking about the specific values of the angles, it is worth noting that the minimum indicator found among the registrars is about 50 ° — this is comparable to the field of view and the degree of magnification of the human eye (excluding side vision). The maximum viewing angle can theoretically reach 180°, however, in fact, navigators use cameras with more modest characteristics — mainly up to 120°.
Sound recording
Possibility of sound recording by the built-in video recorder of the navigator.
In this case, we are talking about sound recording in the cabin. Such a "soundtrack" can give a lot of additional information about the situation recorded by the device. For example, in the event of an accident, it can be established whether the driver was talking on the phone at the time of the accident, when he noticed the danger on the road, how he reacted to it, etc.
In this case, we are talking about sound recording in the cabin. Such a "soundtrack" can give a lot of additional information about the situation recorded by the device. For example, in the event of an accident, it can be established whether the driver was talking on the phone at the time of the accident, when he noticed the danger on the road, how he reacted to it, etc.
G-sensor
A sensor that monitors shocks and vibrations acting on the device. The main function of this sensor is to ensure the safety of video footage captured by the DVR in the event of an accident: in the event of a strong impact, typical of a collision or fall, the DVR with a G-sensor automatically saves the previously recorded video to a non-volatile memory protected from overwriting. Thus, materials about an emergency are not only guaranteed to be saved, but with a high probability remain intact even if the navigator itself is damaged.
More features
— GSM/GPRS module. Built-in wireless cellular module, similar to those found in GSM mobile phones. However, unlike phones, in GPS navigators this communication is intended solely for Internet access. Most often it is used to obtain information about traffic jams, although some advanced models may provide the ability to fully view Internet pages through the built-in browser. To use the GSM/GPRS module, as in the case of a mobile phone, you need to purchase a SIM card from a mobile operator.
— Digital camera. The navigator has its own digital camera; in some models there may even be two such cameras, on both sides of the body. The specific functionality of a digital camera(s) may vary depending on the capabilities of the device itself. Thus, most models with a DVR function use a built-in camera (for more details, see “Built-in DVR”). If you have a telephone module (see the corresponding paragraph), the camera can be useful for video communication. Many navigators with this function can also be used for classic photo/video shooting; The image quality, however, is usually relatively low.
— Video player. Ability to use the navigator to play video files. As a rule, we are talking about playing video on your own display - accordingly, the display itself is made in color and quite large for this purpose. This function is found mainly among car navigators (see “Sc...ope”), it is especially appreciated by drivers who have to spend a lot of time waiting - in particular, taxi drivers and truck drivers.
- Voice control. The ability to control the navigator using voice commands. This feature is especially convenient for automobile and motorcycle devices: it allows you to control the device without taking your hands off the controls and without taking your eyes off the road. However, before purchasing such a model, it would not hurt to clarify which languages it supports for voice control.
— Playback images. Ability to use the navigator screen to view graphic files; By default, JPG support is implied; other graphic formats are somewhat less common. A navigator with this function can be used as a digital photo frame - connect an external storage device and view pictures directly, without the participation of a computer. This function can be useful, for example, for viewing photos taken during a trip (when you don’t want to wait to get back to the computer), or for more specific purposes - for example, clarifying navigation data from a scan of a paper map.
— MP3 player. The ability to play audio files with the navigator (most often in MP3 format, hence the name). Playback can occur through headphones or an external audio system (if it is possible to connect them) or through the navigator’s own speaker. Such files can be stored in the device’s own flash memory or on removable memory cards.
— FM transmitter. Low-power FM transmitter with an effective range of several meters. It is one of the simplest ways to connect a navigator to a car's speaker system - just tune the FM receiver of the car radio to the frequency of the transmitter. In this way, you can use the car speakers, for example, to play voice prompts, music (see MP3 player) or the soundtrack of a movie being played (see Video player).
— Barometer. An auxiliary function that allows you to measure atmospheric pressure. It is often used as an additional tool in navigators with the function of measuring altitude using signals from satellites - this ensures increased accuracy of the received data. In addition, data from the barometer can be useful in forecasting the weather for the near future: for example, a sharp drop in pressure usually means worsening weather - even a storm or even a hurricane.
— Digital camera. The navigator has its own digital camera; in some models there may even be two such cameras, on both sides of the body. The specific functionality of a digital camera(s) may vary depending on the capabilities of the device itself. Thus, most models with a DVR function use a built-in camera (for more details, see “Built-in DVR”). If you have a telephone module (see the corresponding paragraph), the camera can be useful for video communication. Many navigators with this function can also be used for classic photo/video shooting; The image quality, however, is usually relatively low.
— Video player. Ability to use the navigator to play video files. As a rule, we are talking about playing video on your own display - accordingly, the display itself is made in color and quite large for this purpose. This function is found mainly among car navigators (see “Sc...ope”), it is especially appreciated by drivers who have to spend a lot of time waiting - in particular, taxi drivers and truck drivers.
- Voice control. The ability to control the navigator using voice commands. This feature is especially convenient for automobile and motorcycle devices: it allows you to control the device without taking your hands off the controls and without taking your eyes off the road. However, before purchasing such a model, it would not hurt to clarify which languages it supports for voice control.
— Playback images. Ability to use the navigator screen to view graphic files; By default, JPG support is implied; other graphic formats are somewhat less common. A navigator with this function can be used as a digital photo frame - connect an external storage device and view pictures directly, without the participation of a computer. This function can be useful, for example, for viewing photos taken during a trip (when you don’t want to wait to get back to the computer), or for more specific purposes - for example, clarifying navigation data from a scan of a paper map.
— MP3 player. The ability to play audio files with the navigator (most often in MP3 format, hence the name). Playback can occur through headphones or an external audio system (if it is possible to connect them) or through the navigator’s own speaker. Such files can be stored in the device’s own flash memory or on removable memory cards.
— FM transmitter. Low-power FM transmitter with an effective range of several meters. It is one of the simplest ways to connect a navigator to a car's speaker system - just tune the FM receiver of the car radio to the frequency of the transmitter. In this way, you can use the car speakers, for example, to play voice prompts, music (see MP3 player) or the soundtrack of a movie being played (see Video player).
— Barometer. An auxiliary function that allows you to measure atmospheric pressure. It is often used as an additional tool in navigators with the function of measuring altitude using signals from satellites - this ensures increased accuracy of the received data. In addition, data from the barometer can be useful in forecasting the weather for the near future: for example, a sharp drop in pressure usually means worsening weather - even a storm or even a hurricane.
CPU speed
Clock speed of the processor (CPU) installed in the navigator.
This parameter is often used to evaluate the overall level of the device and the power of its filling: it is believed that a higher frequency, in turn, provides greater computing power and better performance. However, the technical features of the processors are such that a high clock frequency does not always mean a more advanced chip. In addition, the processing power of the entire device depends not only on the CPU, but also on other components — from RAM to the operating system and installed software. So this information plays only a supporting role.
This parameter is often used to evaluate the overall level of the device and the power of its filling: it is believed that a higher frequency, in turn, provides greater computing power and better performance. However, the technical features of the processors are such that a high clock frequency does not always mean a more advanced chip. In addition, the processing power of the entire device depends not only on the CPU, but also on other components — from RAM to the operating system and installed software. So this information plays only a supporting role.
RAM
The amount of random access memory (RAM) installed in the navigator.
The amount of RAM is one of the key parameters of any computer system, directly affecting its performance and computing power. The more RAM installed on board, the better the device will cope with resource-intensive tasks and the more applications you can run on it without noticeable damage to the speed of operation.
Specifically in navigators, performance can be important, for example, when driving at high speed - the “braking” device may be late with a hint, which causes various unpleasant situations to arise. At the same time, paying attention to the amount of RAM only makes sense if an operating system like Android is installed on board.
The amount of RAM is one of the key parameters of any computer system, directly affecting its performance and computing power. The more RAM installed on board, the better the device will cope with resource-intensive tasks and the more applications you can run on it without noticeable damage to the speed of operation.
Specifically in navigators, performance can be important, for example, when driving at high speed - the “braking” device may be late with a hint, which causes various unpleasant situations to arise. At the same time, paying attention to the amount of RAM only makes sense if an operating system like Android is installed on board.
Built-in memory
The amount of built-in memory installed in the navigator.
The amount of data that can be stored in the device directly depends on this indicator. However, it is worth keeping in mind that, on the one hand, a certain amount of built-in memory will inevitably be occupied by the operating system (if there is one), firmware and other programs supplied in the kit; on the other hand, the set of these programs in most cases also includes a preinstalled card. The latter means that the navigator can be used for its intended purpose “out of the box” without installing additional software; and for such an application the built-in memory is guaranteed to be enough. This means that it makes sense to pay attention to the storage capacity primarily if the device will have to work with additional data - from extended maps to photos and videos. This is especially true for models with a full-fledged OS like Windows or Android, which allows the installation of additional applications.
The amount of data that can be stored in the device directly depends on this indicator. However, it is worth keeping in mind that, on the one hand, a certain amount of built-in memory will inevitably be occupied by the operating system (if there is one), firmware and other programs supplied in the kit; on the other hand, the set of these programs in most cases also includes a preinstalled card. The latter means that the navigator can be used for its intended purpose “out of the box” without installing additional software; and for such an application the built-in memory is guaranteed to be enough. This means that it makes sense to pay attention to the storage capacity primarily if the device will have to work with additional data - from extended maps to photos and videos. This is especially true for models with a full-fledged OS like Windows or Android, which allows the installation of additional applications.
Interfaces
— Wi-Fi. A technology originally designed to connect to the Internet through wireless access points; for the same purpose, Wi-Fi is most often used in navigators. Note that not only a stationary router can play the role of an access point, but also a smartphone — many of these gadgets have the appropriate mode. But the specific possibilities of such a connection may be different. One of the most popular features is downloading up-to-date traffic data and other traffic information (see "Features"). In addition, navigators may provide updating maps and firmware via the Internet. And for models with full-fledged OS (see "Operating System"), the ways of using Wi-Fi are very diverse: web surfing, access to social networks and instant messengers, "social" games that involve communication with other players, etc. In fact , in navigators with OS, Wi-Fi capabilities are limited only by the set of installed applications.
— USB. The device has a USB connector. Most often, modern navigators are equipped with compact ports like miniUSB or microUSB, and the main purpose of such ports is to charge the battery and connect to a computer — for example, to update maps. The most advanced models may also provide the connection of external peripherals (for example, a flash drive with map updates or a 3G modem for Internet access), but such features are quite rare, mainly among navigators with a full-fledged OS (see "Opera...ting system").
— Slot for memory cards. A device for reading removable memory cards — most often in the SD or microSD form factor; specific types of supported cards should be specified separately. Such a device (card reader) performs two main functions. Firstly, it allows you to expand the built-in memory of the navigator by supplementing it with external media; at the same time, the capacity of the card can be chosen at your discretion (taking into account the maximum volume — see below). Secondly, the card reader facilitates the exchange of data with other devices — smartphones, tablets, laptops, etc.; this can be useful, for example, for loading maps and other navigation data, for copying recorded tracks, etc. The specific functionality of the card reader should be specified separately.
— Headphone output. The presence in the navigator of a special connector for connecting headphones. Usually the role of such an output is played by a standard 3.5 mm port. Headphones can be used for any tasks related to sound accompaniment — voice prompts, talking on the phone or via the Internet (via Skype, Viber, etc.), listening to music and watching videos, etc. (depending on which functions are provided in the navigator itself). At the same time, the “ears” are especially convenient in two situations: in a noisy environment, when the speaker of the navigator may not be heard over background sounds, and also when it is desirable to avoid unnecessary sounds (for example, if passengers are sleeping in the car).
— Bluetooth. A wireless communication technology designed to connect different devices directly to each other. The method of using such a connection can be different, one of the most popular options in navigators is connecting a wireless headset. Through such a headset, you can hear the voice prompts of the navigator and give commands to it, talk on the phone, listen to music, etc. (specific possibilities, of course, depend on the functionality of the navigator itself). However headsets are more expensive than wired headphones and have a limited operating time (the battery needs to be charged periodically); but they are much more comfortable.
— ANT+. This standard is mainly used to transmit information of a sports and medical nature — heart rate, distance traveled, speed, etc. It is characterized by low power consumption, but has a low bandwidth — up to 60 kbps. For ANT + to work, it must be supported not only by the gadget, but also by the smartphone or other device to which it is connected. At the same time, we note that, in addition to a direct connection to an external device, this standard allows you to build networks from ANT +-compatible devices — including integrate them into smart home systems.
— AV input. Input for connecting a composite (audio + video) analogue signal. With such an input, you can connect an external signal source to the navigator, such as a portable DVD player, a reversing camera (in car navigators), an echo sounder (in marine ones), etc.
— USB. The device has a USB connector. Most often, modern navigators are equipped with compact ports like miniUSB or microUSB, and the main purpose of such ports is to charge the battery and connect to a computer — for example, to update maps. The most advanced models may also provide the connection of external peripherals (for example, a flash drive with map updates or a 3G modem for Internet access), but such features are quite rare, mainly among navigators with a full-fledged OS (see "Opera...ting system").
— Slot for memory cards. A device for reading removable memory cards — most often in the SD or microSD form factor; specific types of supported cards should be specified separately. Such a device (card reader) performs two main functions. Firstly, it allows you to expand the built-in memory of the navigator by supplementing it with external media; at the same time, the capacity of the card can be chosen at your discretion (taking into account the maximum volume — see below). Secondly, the card reader facilitates the exchange of data with other devices — smartphones, tablets, laptops, etc.; this can be useful, for example, for loading maps and other navigation data, for copying recorded tracks, etc. The specific functionality of the card reader should be specified separately.
— Headphone output. The presence in the navigator of a special connector for connecting headphones. Usually the role of such an output is played by a standard 3.5 mm port. Headphones can be used for any tasks related to sound accompaniment — voice prompts, talking on the phone or via the Internet (via Skype, Viber, etc.), listening to music and watching videos, etc. (depending on which functions are provided in the navigator itself). At the same time, the “ears” are especially convenient in two situations: in a noisy environment, when the speaker of the navigator may not be heard over background sounds, and also when it is desirable to avoid unnecessary sounds (for example, if passengers are sleeping in the car).
— Bluetooth. A wireless communication technology designed to connect different devices directly to each other. The method of using such a connection can be different, one of the most popular options in navigators is connecting a wireless headset. Through such a headset, you can hear the voice prompts of the navigator and give commands to it, talk on the phone, listen to music, etc. (specific possibilities, of course, depend on the functionality of the navigator itself). However headsets are more expensive than wired headphones and have a limited operating time (the battery needs to be charged periodically); but they are much more comfortable.
— ANT+. This standard is mainly used to transmit information of a sports and medical nature — heart rate, distance traveled, speed, etc. It is characterized by low power consumption, but has a low bandwidth — up to 60 kbps. For ANT + to work, it must be supported not only by the gadget, but also by the smartphone or other device to which it is connected. At the same time, we note that, in addition to a direct connection to an external device, this standard allows you to build networks from ANT +-compatible devices — including integrate them into smart home systems.
— AV input. Input for connecting a composite (audio + video) analogue signal. With such an input, you can connect an external signal source to the navigator, such as a portable DVD player, a reversing camera (in car navigators), an echo sounder (in marine ones), etc.
Max. memory card / flash drive size
The maximum size of a memory card or USB-drive (flash drive) supported by the navigator.
Removable media can be used for different purposes: downloading maps and software updates, uploading tracks you have covered, playing or copying music and movies (in models with the appropriate capabilities), etc. Specific options for using such media for each model should be clarified separately. And the restrictions on volume are primarily due to the fact that more capacious memory cards and flash drives require more powerful hardware. So you should not exceed this limit: at best, the drive will not work correctly, at worst, hardware failures are possible.
Removable media can be used for different purposes: downloading maps and software updates, uploading tracks you have covered, playing or copying music and movies (in models with the appropriate capabilities), etc. Specific options for using such media for each model should be clarified separately. And the restrictions on volume are primarily due to the fact that more capacious memory cards and flash drives require more powerful hardware. So you should not exceed this limit: at best, the drive will not work correctly, at worst, hardware failures are possible.
Power supply
This paragraph takes into account only the type of autonomous power source (batteries or accumulator).
- Battery. In this case, we mean our own original battery, which is not of a standard size, and in some cases is not removable at all. One of the advantages of this option is that the battery is included in the package and does not need to be purchased separately, unlike batteries. And the use of such a device does not require additional costs - a dead battery just needs to be charged. However, the main disadvantage of such power is also that when the charge is depleted, the device will have to be charged - and this requires time and a power source. However, it is worth noting that most battery models are designed to work in a car or motorcycle and have the ability to connect to a 12 V network. As a result, most of the time such a navigator receives power from the car, and the battery is used only when disconnected from the on-board network. So the mentioned drawback can hardly be called critical.
— Batteries. Powered by replaceable elements of a standard size - for example, “finger-type” AA. Note that among such elements there are both disposable batteries and rechargeable batteries. This gives the user a choice: regularly purchase fresh elements or spend money once on batteries and a “charger” for them. However, in any case, power from batteries is associated with additional costs - such power supplies are usually n...ot included in the kit, and they have to be purchased separately. At the same time, this option has an important advantage: a dead battery can be quickly replaced with a fresh one. This option is found mainly among universal models.
- Battery. In this case, we mean our own original battery, which is not of a standard size, and in some cases is not removable at all. One of the advantages of this option is that the battery is included in the package and does not need to be purchased separately, unlike batteries. And the use of such a device does not require additional costs - a dead battery just needs to be charged. However, the main disadvantage of such power is also that when the charge is depleted, the device will have to be charged - and this requires time and a power source. However, it is worth noting that most battery models are designed to work in a car or motorcycle and have the ability to connect to a 12 V network. As a result, most of the time such a navigator receives power from the car, and the battery is used only when disconnected from the on-board network. So the mentioned drawback can hardly be called critical.
— Batteries. Powered by replaceable elements of a standard size - for example, “finger-type” AA. Note that among such elements there are both disposable batteries and rechargeable batteries. This gives the user a choice: regularly purchase fresh elements or spend money once on batteries and a “charger” for them. However, in any case, power from batteries is associated with additional costs - such power supplies are usually n...ot included in the kit, and they have to be purchased separately. At the same time, this option has an important advantage: a dead battery can be quickly replaced with a fresh one. This option is found mainly among universal models.
Battery life
The operating time of the navigator on one battery charge or a set of batteries depends on the power source (see above).
This parameter is more visual and closer to reality than technical information about the type of batteries, battery capacity, etc. However note that the operating time is usually indicated for a conditional perfect situation: a good signal level without the need to reconnect, low screen brightness ( or completely turned off the backlight), minimal use of wireless modules (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), etc. Practical conditions inevitably differ from perfect — accordingly, the operating time may differ noticeably from the claimed one (usually in the direction of reduction, but sometimes vice versa) . Nevertheless, the operating time stated in the characteristics is quite reliable information, and it is quite possible to evaluate the capabilities of the selected device, as well as compare it with other models.
This parameter is more visual and closer to reality than technical information about the type of batteries, battery capacity, etc. However note that the operating time is usually indicated for a conditional perfect situation: a good signal level without the need to reconnect, low screen brightness ( or completely turned off the backlight), minimal use of wireless modules (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), etc. Practical conditions inevitably differ from perfect — accordingly, the operating time may differ noticeably from the claimed one (usually in the direction of reduction, but sometimes vice versa) . Nevertheless, the operating time stated in the characteristics is quite reliable information, and it is quite possible to evaluate the capabilities of the selected device, as well as compare it with other models.
Battery capacity
This parameter directly determines the amount of energy that the battery can store; and the greater the energy reserve, the longer the device can work on one battery charge. However, this is in theory; in practice the situation is somewhat more complicated. Firstly, the actual autonomy of the navigator will also depend on the power consumption of the device - and it can vary greatly between different models. Secondly, milliamp-hours, in which capacity is indicated, is not a completely reliable unit: the physical features of such a designation are such that two batteries with the same capacity in mAh, but different nominal voltages, will also have different actual amounts of stored energy.
In light of all this, it is hardly worth assessing the autonomy of the navigator by the capacity of the included battery - it is better to look at the operating time directly stated by the manufacturer.
In light of all this, it is hardly worth assessing the autonomy of the navigator by the capacity of the included battery - it is better to look at the operating time directly stated by the manufacturer.
Magnetic mount
The device holder is in the form of a permanent powerful magnet, the strength of which is sufficient to hold the navigator in place. To install the device on such a clamp, it is enough to “stick” the navigator to the magnetic pad, and to remove it, pull it firmly. Magnetic mounts are very easy to use, reliable and durable due to the absence of moving parts in the design.