How to choose a processor for a video card and vice versa
We independently test the products and technologies that we recommend.

1. What are the processor and video card responsible for in games (and not only)
When you start a demanding video game or edit a video, your computer is working at full capacity. At these moments, it is the processor ( CPU) and the video card ( GPU) that take on the main load, performing complex calculations and processing graphics. The processor is the “brain” of the computer, performing all the calculations and managing the system. The video card, in turn, is the “eyes” responsible for the visual part - rendering graphics and video.

the i3-9100F processor limits the 2080 Ti video card,
without having time to transmit all the necessary data to it.
The pair works like the cop duo in Lethal Weapon, with Glover’s more experienced Danny planning and assessing risks while Mel Gibson’s impulsive hero takes action. In games, the CPU handles a wide range of tasks, including performing AI calculations, processing level geometry, physics calculations (such as when a character interacts with water), and managing the behavior of particles like snow or sparks. It also performs arithmetic operations and control functions that are critical to the overall functioning of the system.
The video card, in turn, specializes in graphics processing. It is responsible for creating and displaying textures, lighting, shadows and reflections, as well as rendering complex post-processing effects. The GPU supports modern technologies such as Ray Tracing to create photorealistic visual effects. The smoothness and detail of the image depend on the capabilities of the video card, directly affecting the quality of the graphics and the level of immersion in the game. Without a high-flow Rate video card, the game image can become an unpleasant slide show with falling textures and noticeable delays in complex scenes.
2. How does the role of the processor and video card change depending on the tasks?
Without the right balance between the CPU and GPU, a so-called “bottleneck” can occur, where one component limits the flow Rate of the other. It’s important to understand that there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to choosing a processor and graphics card. Your perfect choice will depend on how you plan to use your computer. Will you be exclusively gaming, working with graphics or programming, or perhaps want a versatile machine that can handle any task?
Games
For gamers, the processor and graphics card are key components that determine how smoothly and beautifully the game will run. An ancient and weak Core i3-8100 with 4 cores simply will not be able to reveal the potential of a flagship graphics card like the GeForce RTX 4080, since its computing power is not enough to ensure the stable operation of high-flow Rate graphics solutions. As a result, the processor will become a bottleneck, and the graphics card will not be able to show its true potential.
Rendering
In contrast, in “professional” tasks such as video rendering or 3D modeling, the video card comes to the fore. It is responsible for performing intensive graphical calculations, such as processing complex textures, creating detailed 3D objects, and applying lighting and shadow effects. These tasks require high GPU flow Rate, allowing for a significant reduction in rendering time and acceleration of the process of creating graphical content. The processor is of lesser importance in such cases, because its role is limited to supporting the operation of the video card and managing auxiliary tasks.
Multi-threaded processing
Well, for processing large amounts of data and multitasking, a powerful processor is more important because it is responsible for performing all calculations and operations that require high computing resources, such as data analysis, running virtual machines and executing parallel tasks. The processor ensures efficient distribution of tasks between threads and cores, allowing for faster data processing, improved flow Rate in multitasking scenarios and higher overall system efficiency.
3. How to avoid bottlenecks when choosing components?
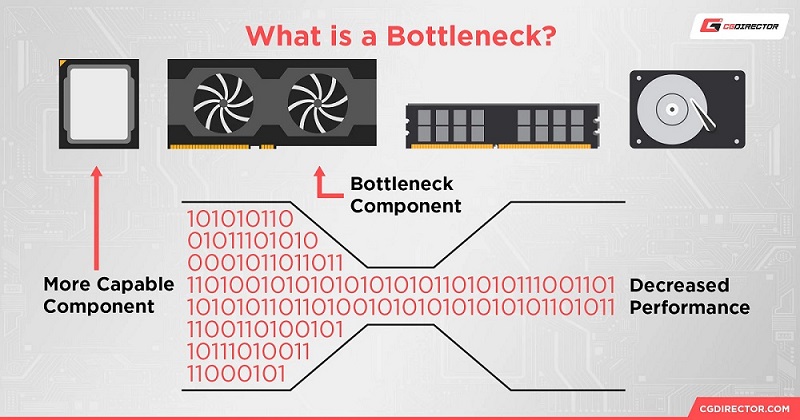
To prevent bottlenecks, it is important to properly balance the processor and graphics card. Here are a few steps to help you find the perfect combination:
- Determine the primary purpose of your PC. If you plan to play modern games, choose a processor and graphics card that match each other in flow Rate. For example, to unleash the potential of the flagship GeForce RTX 4080 graphics card, you will need a powerful processor like the Intel Core i7 13700K or AMD Ryzen 7 7800X.
- Research component compatibility. Use online calculators like Bottleneck Calculator or PCPartPicker to get an idea of how well your chosen CPU and graphics card will work together. These tools analyze component flow Rate and provide compatibility recommendations. You can also check out reviews and benchmarks on specialist sites to see how specific component pairs perform in real-world conditions.
- Performance monitoring. After assembling your PC, you can monitor the load on the processor and video card in games and profile applications. This can be done using the regular Windows task manager (the "Productivity" tab) or using a profile utility such as MSI Afterburner or HWMonitor. If one component is consistently loaded at 100% while the other is running at a less intensive mode, this may indicate a bottleneck. In such cases, consider upgrading the less productive component.
- Periodic update. Keep in mind that flow Rate requirements may change over time. Periodically check whether your components are powerful enough for current tasks and games. For example, the old Ryzen 2600X feels quite comfortable in modern games, while video cards of tech years, like the popular GeForce GTX 1060, are clearly lagging behind the requirements of modern game engines. Especially if you play not in 1080p, but in a higher resolution of 1440p or 2160p.
4. Recommendations for choosing a processor and video card

For games
Choose a processor and a graphics card that are balanced in flow Rate. Make sure that the processor does not become a bottleneck for the graphics card, and the graphics card does not overload the processor. For example, modern games require not only a powerful graphics card, but also a fast processor that can support its capabilities. Determine the type of games you plan to play. For example, shooters and action games require a high frame rate, so focus on graphics cards with good flow Rate at 1080p or higher. For strategies and simulators, processor power is more important.
For professional tasks
For rendering and 3D modeling tasks, choose video cards with a large number of CUDA cores (NVIDIA) or stream processors (AMD). Pay attention to the video memory, which should be sufficient for your tasks. The processor must support the operation of the video card and perform auxiliary calculations, so choose models with a high clock speed and number of cores.
For multitasking and processing large amounts of data
For efficient multitasking and big data processing, choose a processor with a high number of cores and threads, as well as a high clock speed. Models with 8 or more cores and a frequency above 4 GHz provide fast data processing and efficient task distribution. This will ensure faster information processing, launching virtual machines, and simultaneous execution of several tasks. The video card is less critical in this case if your tasks do not require intensive graphics processing. For example, for multitasking and data processing, a mid-range video card like the GeForce RTX 3060 Ti is quite suitable in combination with the flagship Intel Core i9-13900K processor.

AMD Threadripper server processor and water cooling.
Below you can see several examples of optimal CPU + GPU combinations for different tasks and budgets:
- Low cost Gaming PC
- Processor: AMD Ryzen 5 5600G
- Video card: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650 This bundle is suitable for gaming in Full HD at medium settings. Provides a good price/flow Rate ratio for modern games and basic tasks.
- Middle segment
- Processor: Intel Core i5-13600K
- Video card: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti A great choice for gaming in Full HD and 1440p at high settings. Also suitable for basic video and 3D graphics work.
- High segment
- Processor: AMD Ryzen 7 7800X
- Video Card: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 This combination will allow you to game at 1440p and 4K on high settings, as well as do rendering and graphic design.
- Professional level
- Processor: Intel Core i9-13900K
- Video Card: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 Ideal choice for high resolutions, intensive rendering, video editing and complex computing tasks.
- Expert level
- Processor: AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 5975WX
- Video card: NVIDIA RTX A6000 A professional bundle for workstations that require massive computing power and multitasking, such as 3D modeling and complex calculations.
5. Final touches: checking compatibility

Once you've chosen your processor and graphics card, it's important to make sure they're compatible with the other components in your PC. Here are some key things to consider:
- Motherboard: Make sure your motherboard supports the processor and graphics card you've chosen. Check that the motherboard has the appropriate processor socket and enough PCIe slots to connect and power the graphics card.
- Dimensions: Make sure your PC case is large enough to accommodate the graphics card and a tower cooler for the CPU. Some modern graphics cards can be quite large, so check the dimensions before buying, especially if you have a compact case. However, in most cases there will be no reason to worry, since most modern graphics cards are no longer than 330 mm, and most modern cases are designed for these dimensions.
- Power: Make sure that the power supply has enough power and the necessary connectors to connect the processor and the video card. Especially if you plan to buy a new GPU with ATX 3.0 power specifications that require the appropriate power connectors. As for power, video card manufacturers usually specify the required power of the power supply with a small reserve so that it does not work in a constant 100% load mode.
- Cooling: Make sure your case has enough fans and proper air cooling to maintain optimal temperatures. Particularly demanding graphics cards will need powerful case cooling, while flagship CPUs with 20 or more cores may require a high-flow Rate liquid cooling system. A good option for a mid-range gaming or workstation build might be an Airflow case with a perforated cover and several pre-installed fans, like the MSI MAG FORGE M100R.
6. Conclusion

To sum it up, it is important to remember that the choice of a processor and a graphics card should be based on the balance of components for your tasks. The right combination ensures maximum flow Rate and avoids bottlenecks. Don’t forget to check the compatibility of all components, including the motherboard, power supply, and cooling system, to avoid problems during assembly. Regularly monitor the system’s flow Rate and be prepared to upgrade components if they start to lag behind modern requirements. If you have more specific questions about choosing individual components, the guides “How to choose a processor” and “How to choose a graphics card” are at your service.
Was this article useful? Yes0 No0 |
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials